It was a great week! Let me share a group picture from the event:

Developer of the CRYSTAL code!
It was a great week! Let me share a group picture from the event:

Hi,
If I am not mistaken, "total atomic spins" are indeed reported in units of the Bohr magneton and are obtained from a Mulliken partitioning of the spin density (i.e. difference between the electron density of spin-up and spin-down electrons).
Cheers,
Hi Drmajouri2025,
When performing frequency calculations, it is essential that the geometry is fully optimized with the SCF properly converged. If the structure is not at a true stationary point of the potential energy surface, the computed second derivatives (Hessian) can lead to unreliable frequencies and response properties.
Regarding the *******************, these typically means that the value exceeds the field width allocated in the printing format. In other words, the number is too large (or not representable) within the fixed output format, so it is replaced by stars.
However, in your case, since the geometry did not converge properly, the appearance of stars is very likely due to numerical problem rather than just a harmless formatting issue.
I would strongly recommend:
TOLDEE and/or TOLINTEG parameters).Dear user,
as noted by GiacomoAmbrogio, we invite you to use CRYSTALClear, which is the Python framework that we currently maintain and support. Regarding your question, yes: you should use BAND.DAT as the *.BAND file and OUTPUT as the *.out file.
Hi,
I suggest you to use CRYSTALClear instead. Here you can find an installation guide, and on the GitHub page there is the documentation and some example notebooks that you can use as template.
For any question related to CRYSTALClear there is a dedicated section here on the forum.
Hi,
We have run some tests and we have identified the origin of the problem. The calculation fails in the evaluation of the Fermi energy in the NEWK option (so before getting to the BOLTZTRA step) because of large memory requirements due to a very large number of k-points being asked and because of the replicated-memory parallel implementation of that bit of code.
In that part of the code, with Pproperties (parallel version), data are replicated in memory by each process.
We have run tests on this system in parallel with different number of processes (on a computing node with 128 CPU cores) and for different shrinking factor parameters of the NEWK keyword. Results are summarized in the table below:
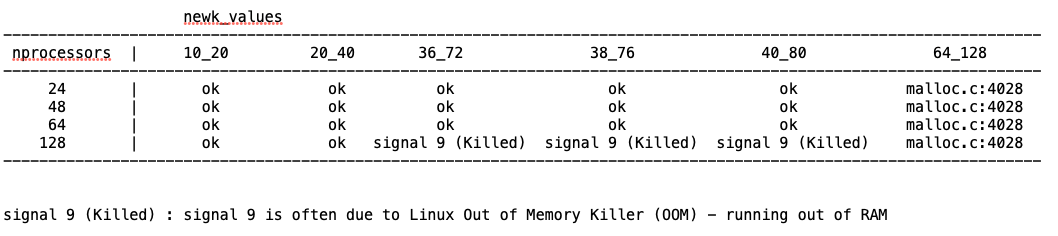
"ok" marks combinations for which the calculation run without errors. The trend is clear and can be rationalized as follows:
Hope this clarifies things and helps find a way forward,
Hi,
I used space group 186 for ZnO that corresponds to the one you mention. In the character table printed by CRYSTAL only those irreps that are actually used to build symmetry-adapted Bloch functions are shown. I have updated my original post above to show the irrep labels in the character tables, which match those found in the printing of the eigenvalues.
Hope this clarifies things,
Dear CRYSTAL community,
The CRYSTAL Team is heading to Brazil! 

Next week (26th Jan – 29th Jan 2026), we will be in Volta Redonda (Rio de Janeiro state) for the

QMMC 2026 will be hosted at the Universidade Federal Fluminense and it will be an exciting journey through quantum modelling of materials, covering a wide range of topics in computational chemistry and condensed matter physics.
We are truly excited to be in Volta Redonda and to share knowledge, experience, and, of course, to spread the CRYSTAL verb!
More information about the school can be found on the event website.
See you in Brazil!
Hi,
The following keyword combination to be inserted in the third block of the .d12 CRYSTAL input file works for me on a 3D crystal (I have tried on ZnO as a test):
SETPRINT
2
47 10
66 10
KSYMMPRT
The keyword KSYMMPRT activates a printing level with character tables for the various k little groups. With SETPRINT you set other printing options: option 47 refers to KSYMMPRT while option 66 activates the printing of the eigenvalues. With 10 in both cases I am asking for detailed printing for the first 10 k points in the list. Just increase this parameter from 10 to X for detailed information on the first X k points.
At the end of the SCF, in the output file you will find detailed symmetry information. For ZnO, for instance:
+++ SYMMETRY ADAPTION OF THE BLOCH FUNCTIONS +++
SYMMETRY INFORMATION:
K-LITTLE GROUP: CLASS TABLE, CHARACTER TABLE.
IRREP-(DIMENSION, NO. IRREDUCIBLE SETS)
(P, D, RP, RD, STAND FOR PAIRING, DOUBLING, REAL PAIRING AND REAL DOUBLING
OF THE IRREPS (SEE MANUAL))
CLASS | GROUP OPERATORS (SEE SYMMOPS KEYWORD)
--------------------------------------------------------------------
C2 | 2;
C3 | 3; 4;
C6 | 5; 6;
SGV | 7; 8; 9;
SGV' | 10; 12; 11;
IRREP/CLA E C2 C3 C6 SGV SGV'
---------------------------------------------------
MULTIP | 1 1 2 2 3 3
---------------------------------------------------
A | 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00
B | 1.00 -1.00 1.00 -1.00 1.00 -1.00
E1 | 2.00 -2.00 -1.00 1.00 0.00 0.00
E2 | 2.00 2.00 -1.00 -1.00 0.00 0.00
A -(1, 21); B -(1, 21); E1 -(2, 15); E2 -(2, 15);
CLASS | GROUP OPERATORS (SEE SYMMOPS KEYWORD)
--------------------------------------------------------------------
C2 | 8;
IRREP/CLA E C2
-----------------------
MULTIP | 1 1
-----------------------
A | 1.00 1.00
B | 1.00 -1.00
A -(1, 72); B -(1, 30);
[...]
And information about the eigenvalues at each k point with the associated irrep symmetry label:
FINAL EIGENVALUES (A.U.)
(LABELS REFER TO SYMMETRY CLASSIFICATION)
1 ( 0 0 0)
-3.4563E+02(B ) -3.4563E+02(A ) -4.1575E+01(B ) -4.1575E+01(A ) -3.6643E+01(A )
-3.6643E+01(B ) -3.6643E+01(E1 ) -3.6643E+01(E1 ) -3.6642E+01(E2 ) -3.6642E+01(E2 )
-1.8704E+01(A ) -1.8704E+01(B ) -4.5481E+00(A ) -4.5481E+00(B ) -2.9815E+00(B )
-2.9814E+00(A ) -2.9812E+00(E2 ) -2.9812E+00(E2 ) -2.9812E+00(E1 ) -2.9812E+00(E1 )
-8.2115E-01(A ) -7.9663E-01(B ) -3.8298E-01(E1 ) -3.8298E-01(E1 ) -3.8023E-01(A )
-3.7674E-01(E2 ) -3.7674E-01(E2 ) -3.6589E-01(B ) -3.4625E-01(E1 ) -3.4625E-01(E1 )
-3.3970E-01(E2 ) -3.3970E-01(E2 ) -3.2752E-01(B ) -2.0184E-01(E2 ) -2.0184E-01(E2 )
-1.7704E-01(A ) -1.7506E-01(E1 ) -1.7506E-01(E1 ) -1.3296E-01(A ) 2.8917E-02(B )
1.3748E-01(B ) 3.0394E-01(E1 ) 3.0394E-01(E1 ) 3.4544E-01(E2 ) 3.4544E-01(E2 )
3.5105E-01(A ) 7.3399E-01(A ) 7.9567E-01(B ) 7.9827E-01(E2 ) 7.9827E-01(E2 )
8.0430E-01(E1 ) 8.0430E-01(E1 ) 9.2452E-01(E1 ) 9.2452E-01(E1 ) 9.4481E-01(A )
1.0085E+00(E2 ) 1.0085E+00(E2 ) 1.0835E+00(B ) 1.1254E+00(A ) 1.4388E+00(E2 )
1.4388E+00(E2 ) 1.5197E+00(E1 ) 1.5197E+00(E1 ) 1.5953E+00(B ) 1.6980E+00(A )
1.9424E+00(B ) 2.1214E+00(B ) 2.4581E+00(E2 ) 2.4581E+00(E2 ) 2.6850E+00(A )
2.6884E+00(E1 ) 2.6884E+00(E1 ) 2.6992E+00(B ) 2.7357E+00(E1 ) 2.7357E+00(E1 )
2.7753E+00(E2 ) 2.7753E+00(E2 ) 3.0348E+00(E2 ) 3.0348E+00(E2 ) 3.1219E+00(E1 )
3.1219E+00(E1 ) 3.1318E+00(A ) 4.2450E+00(E2 ) 4.2450E+00(E2 ) 4.2830E+00(A )
4.4957E+00(E1 ) 4.4957E+00(E1 ) 4.5498E+00(E1 ) 4.5498E+00(E1 ) 4.7190E+00(B )
4.7730E+00(E2 ) 4.7730E+00(E2 ) 4.7949E+00(A ) 4.8374E+00(E2 ) 4.8374E+00(E2 )
4.8743E+00(B ) 5.0462E+00(E1 ) 5.0462E+00(E1 ) 5.4477E+00(A ) 5.8198E+00(B )
3.9355E+01(B ) 3.9424E+01(A )
2 ( 1 0 0)
-3.4563E+02(A ) -3.4563E+02(A ) -4.1575E+01(A ) -4.1575E+01(A ) -3.6643E+01(A )
-3.6643E+01(A ) -3.6643E+01(B ) -3.6642E+01(A ) -3.6642E+01(B ) -3.6642E+01(A )
-1.8704E+01(A ) -1.8704E+01(A ) -4.5481E+00(A ) -4.5481E+00(A ) -2.9815E+00(A )
-2.9814E+00(A ) -2.9812E+00(A ) -2.9812E+00(B ) -2.9812E+00(A ) -2.9812E+00(B )
-8.1833E-01(A ) -7.9542E-01(A ) -3.8502E-01(A ) -3.8129E-01(B ) -3.7873E-01(A )
-3.7647E-01(A ) -3.7434E-01(B ) -3.6339E-01(A ) -3.4716E-01(A ) -3.4630E-01(B )
-3.3948E-01(B ) -3.3567E-01(A ) -3.2769E-01(A ) -2.2123E-01(A ) -2.0904E-01(B )
-2.0238E-01(A ) -1.8061E-01(A ) -1.7889E-01(B ) -9.9076E-02(A ) 5.0288E-02(A )
1.3868E-01(A ) 2.6653E-01(A ) 3.0802E-01(B ) 3.1234E-01(A ) 3.5046E-01(B )
3.5371E-01(A ) 7.3602E-01(A ) 7.7587E-01(B ) 7.9991E-01(A ) 8.0492E-01(A )
8.3924E-01(B ) 8.5620E-01(A ) 9.3227E-01(A ) 9.3403E-01(B ) 9.5348E-01(A )
9.9448E-01(A ) 1.0316E+00(B ) 1.1292E+00(A ) 1.1707E+00(A ) 1.3826E+00(A )
1.4008E+00(B ) 1.5217E+00(B ) 1.5347E+00(A ) 1.6362E+00(A ) 1.7168E+00(A )
1.9795E+00(A ) 2.1273E+00(A ) 2.4524E+00(B ) 2.4562E+00(A ) 2.6427E+00(A )
2.6752E+00(B ) 2.6832E+00(A ) 2.6862E+00(A ) 2.7057E+00(B ) 2.7063E+00(A )
2.7671E+00(B ) 2.7722E+00(A ) 2.9842E+00(A ) 3.0206E+00(B ) 3.0849E+00(A )
3.1311E+00(B ) 3.1382E+00(A ) 4.2311E+00(A ) 4.2454E+00(B ) 4.2544E+00(A )
4.4759E+00(B ) 4.4850E+00(A ) 4.5531E+00(B ) 4.5945E+00(A ) 4.6563E+00(A )
4.7965E+00(A ) 4.8056E+00(B ) 4.8150E+00(B ) 4.8262E+00(A ) 4.9013E+00(A )
4.9403E+00(A ) 5.0500E+00(B ) 5.0510E+00(A ) 5.5124E+00(A ) 5.8464E+00(A )
3.9366E+01(A ) 3.9416E+01(A )
[...]
Hope this helps,
Hi,
Thank you for reporting this.
While we run some tests on our cluster, may I suggest switching from a coupled-perturbed Kohn-Sham (CPKS) approach to a Berry phase (BP) approach for the IR intensities? The latter is way less computationally demanding than the former and in this case could be beneficial to the success of the calculation.
You are currently using CPKS as per your input file:
FREQCALC
NOECKART
INTENS
INTCPHF
FMIXING
60
ANDERSON
MAXCYCLE
300
ENDCPHF
ENDFREQ
To switch to BP, you can use instead:
FREQCALC
NOECKART
INTENS
ENDFREQ
Let me know how this goes,